Jurats vs. Oaths
In the legal realm, particularly within the context of affidavits and similar documents, two terms often arise: "jurats" and "oaths." While they both play crucial roles in affirming the validity and truthfulness of statements, they serve distinct purposes. Let's delve into each to understand their differences and significance.
Jurats:
A jurat is a certification or verification added to a document, typically an affidavit, to affirm that the document was duly sworn or affirmed by the person whose signature appears on it. The purpose of a jurat is to ensure the authenticity and validity of the statements made within the document. It involves the following key elements:
Swearing or Affirming: Before a notary public or another authorized official, the individual making the statements in the document must swear or affirm that the contents are true and accurate to the best of their knowledge.
Signature and Seal: Once the individual has sworn or affirmed the statements, they sign the document in the presence of the notary or other authorized official. The official then completes the jurat by adding their signature, seal, and the date.
Statement by the Notary: The notary or authorized official also includes a statement indicating that the individual appeared before them, swore or affirmed the statements, and signed the document in their presence.
Jurats are commonly used in legal proceedings, real estate transactions, and various official documents where the truthfulness of statements is crucial.

Oaths:
An oath, on the other hand, is a solemn pledge or promise to tell the truth or fulfill a duty. Unlike a jurat, which is a certification process added to a document, an oath is an oral or written declaration made by an individual before giving testimony or assuming a position of responsibility. Key aspects of oaths include:
Solemnity: Oaths are administered with a sense of solemnity and seriousness. They often involve invoking a higher authority or making a promise based on one's honor.
Legal and Ethical Obligations: By taking an oath, individuals commit to upholding legal and ethical standards. This commitment underscores the importance of honesty, integrity, and responsibility in various contexts, such as court proceedings, public office, or professional roles.
Legal Consequences: Breaking an oath can have legal consequences, such as perjury charges in a court of law. Therefore, the act of taking an oath carries significant weight and is not to be taken lightly.
Oaths are deeply ingrained in legal, political, and ceremonial practices, serving to uphold principles of truthfulness, accountability, and trustworthiness in society.
Oath Spoken by an Individual

Oath Administered by an Authorized individual/Notary Public

Key Differences:
While both jurats and oaths involve affirmations of truthfulness, they differ in their execution and purpose:
- Jurats are certifications added to documents, verifying that the statements within them have been sworn or affirmed before an authorized official.
- Oaths, on the other hand, are solemn pledges or promises made by individuals, often before assuming a duty or giving testimony, and can have legal implications if violated.
In essence, jurats authenticate documents, while oaths affirm personal integrity and commitment to truth.
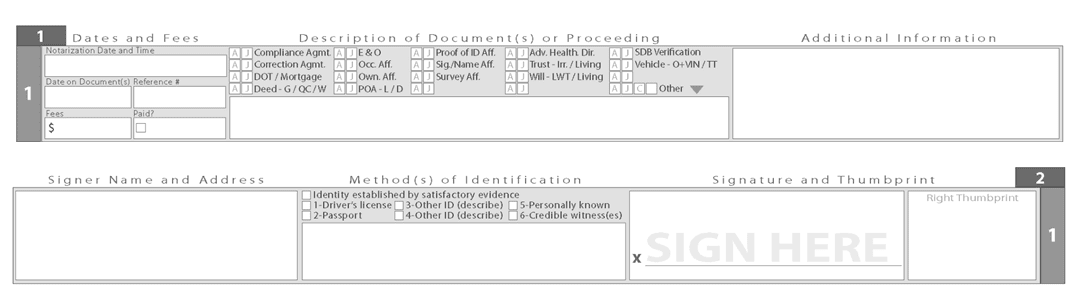
Recording in the Notary's Journal:
In addition to their distinct roles, both jurats and oaths share another commonality: they are recorded in the notary's journal as notarial acts. The notary public or authorized official is required to maintain a detailed record of all notarial acts performed, including jurats and oaths.
Even though a jurat involves certifying a document, and an oath may not always involve a physical document, both actions are considered significant notarial acts. The recording in the notary's journal serves as a crucial record of the proceedings, providing a comprehensive account of the individuals involved, the nature of the act performed, and any relevant details.
By documenting jurats and oaths in the notary's journal, transparency, and accountability are upheld, ensuring that the notarial process maintains its integrity and legality. Additionally, the journal serves as a valuable resource for legal authorities, should the need arise to verify or review the notarial acts conducted by the notary public.
Sample Journal from the Modern Journal of Notarial Events
In conclusion, understanding the disparity between jurats and oaths is vital in legal and professional settings where accuracy, honesty, and accountability are paramount. Whether certifying the truthfulness of statements in a document or solemnly pledging to uphold one's responsibilities, both processes contribute to the integrity and reliability of legal proceedings and societal interactions.

